Everything posted by abbalolucky
-
New Chrome Vulnerability Could Let Hackers Escape Browser Security
New Chrome Vulnerability Could Let Hackers Escape Browser Security – What You Need to KnowA newly discovered security flaw in Google Chrome is drawing serious attention from cybersecurity experts around the world, and Nigerians using Chrome browsers are advised to take immediate action by updating their browsers. The issue, discovered in the browser's graphics handling system, has already been exploited by attackers online—making it a real threat to users. The flaw is associated with Chrome's rendering engine and its interaction with GPU hardware, which can allow malicious actors to bypass built-in browser protections and execute code outside the browser sandbox. This type of vulnerability is especially dangerous because attackers can trigger it just by tricking users into visiting a malicious website. No downloads or clicks are required—the compromise happens in the background, silently and instantly. What’s the Risk?This specific flaw lies in Chrome’s ANGLE (Almost Native Graphics Layer Engine), a component that translates browser rendering tasks into commands that the underlying graphics hardware can understand. If this process is not properly secured, attackers can exploit the low-level GPU instructions to escape the browser sandbox. The sandbox is designed to isolate code execution from the rest of the system, preventing malware from accessing sensitive files or system resources. When a sandbox escape occurs, the attacker may gain privileges beyond the browser itself—opening the door to spying, data theft, or installation of malware. This vulnerability allows remote attackers to craft a special HTML page that exploits this weakness, turning the browser into a launchpad for further attacks. Who Found It?The issue was identified by researchers from Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG), who specialize in investigating government-backed hacking and advanced persistent threats (APT). The fact that the flaw was discovered by this particular team suggests it may have been used in highly targeted attacks, possibly involving nation-state actors. Although Google hasn’t released full technical details, the company confirmed that the vulnerability is being actively used in real-world attacks. This marks yet another instance in a growing trend of high-severity Chrome zero-day vulnerabilities being discovered and patched mid-year. Similar Issues in the PastThis incident follows another zero-day vulnerability fixed just weeks prior. Google has already patched at least five high-impact flaws in Chrome this year alone, many of which were considered critical. These types of vulnerabilities are often linked to bugs in graphics rendering, memory management, and privilege boundary violations—key areas of concern for browser developers and security teams alike. While Chrome is the main focus, it's important to understand that other Chromium-based browsers, including Microsoft Edge, Brave, Opera, and Vivaldi, also share much of the same codebase. This means they are potentially vulnerable to similar attacks until they release their own patches. What Should Users Do?Nigerian users, especially those handling sensitive data such as in banking, government, education, and tech, should prioritize updating their Chrome browser immediately. The patched versions—138.0.7204.157 and above—are now available for Windows, macOS, and Linux platforms. To update: Open Chrome. Click the three-dot menu in the top-right corner. Go to Help > About Google Chrome. Chrome will automatically check for updates and install the latest version. Click Relaunch to complete the update. If you're using other browsers like Edge or Brave, ensure you're using the most recent version or check for security updates from the official sources. Stay SecureCyber threats are evolving fast, and browser exploits like this demonstrate how even everyday activities like browsing the web can become risky. Keeping your browser updated, avoiding suspicious links, and using a reputable antivirus solution are essential steps for staying protected. For cybersecurity professionals, this case is another reminder that GPU and rendering-related vulnerabilities are gaining traction among attackers and should be monitored closely in future research and assessments.
-
Major Security Risk: Attackers Exploit Cisco Software Used in Company Networks
🚨Major Security Risk: Attackers Exploit Cisco Software Used in Company NetworksA new warning has been issued for businesses and organizations using Cisco's Identity Services Engine (ISE). Security experts have discovered that hackers are actively attacking weak spots in this software, and if your system is not updated, attackers could gain full control. What is Cisco ISE?Cisco ISE is a security tool that helps businesses manage who is allowed into their internal computer systems. It checks the identity of users and devices before allowing them access. Many Nigerian businesses and institutions use Cisco products for network control, making this issue especially important to understand. What's the Problem?Researchers found serious weaknesses in Cisco ISE and its related software. These weaknesses are called vulnerabilities. Hackers have started taking advantage of them to break into systems without needing any password or login information. Once inside, they can control the whole system like an administrator. What Can Hackers Do With This?If your Cisco ISE is affected and not updated, hackers can: Run harmful commands on your server. Install malicious files that give them ongoing control. Gain full access as a “root” user, which is the highest level of access. Avoid detection by using the same tools the system uses for trusted users. How Are These Attacks Happening?There are three main problems (security experts call them CVEs): Improper Input Checking Some APIs (the parts of the software that talk to other software) are not checking input correctly. Hackers can send specially crafted commands and run programs as if they were administrators. File Upload Trick In some versions, an attacker can upload a file and place it in a sensitive part of the system. Once the file is there, they can run it to gain full access. Lack of Validation The software fails to block dangerous files from being uploaded, allowing an attacker to bypass security protections. Who Is at Risk?Any organization using Cisco ISE or ISE-PIC and hasn’t updated their software is at risk. This includes: Banks and financial institutions Government agencies Universities and private schools Hospitals and medical centers Internet service providers and large businesses What Should You Do?If you are managing a system using Cisco ISE: Update your software immediately. Cisco has released new versions that fix the problem. Check your system logs. Look for strange activity, like unknown users, unexpected file uploads, or abnormal API requests. Limit external access. Don’t expose the system to the internet unless absolutely necessary. Talk to your security team. Make sure everyone is aware of the risk and the steps taken to reduce it. Staying updated and informed is key to protecting your network, especially with these types of high-risk flaws.
-
How Hackers Are Exploiting Online Shops and Servers to Earn Illegal Money
How Hackers Are Exploiting Online Shops and Servers to Earn Illegal Money Cybercriminals are now turning to online store platforms like Magento and server tools such as Docker to secretly make money. These attackers are not just randomly picking their targets — they are skilled, organized, and always searching for new ways to break into websites and systems that are not properly protected. One known group of attackers, who have previously targeted websites built with a system called Craft CMS, has now moved on to bigger platforms like Magento (an e-commerce system) and Docker (used for running apps on servers). Their main goal is to make money by hijacking the power of other people's computers and internet connections. How the Attack WorksThese hackers find weak spots in the software used by businesses and developers. One method involves using a bug in a Magento plugin to run dangerous commands through a feature called PHP-FPM. This gives them access to the server. Once inside, they install a special tool called GSocket. It hides in the system like a normal background process, making it difficult to notice. GSocket allows the attackers to connect to the hacked machine anytime they want, even after reboots. What’s more troubling is their use of in-memory techniques. Instead of saving files that security tools can detect, they run their malware directly from memory using advanced Linux functions like memfd_create(). This allows them to load additional tools like: XMRig – a program used to mine cryptocurrency using the victim’s CPU power. IPRoyal Proxyware – software that sells the victim’s internet connection to other people without permission. To stay hidden, the hackers even modify critical system files like /etc/ld.so.preload to inject rootkits that make their tools invisible. This means even if the crypto miner is found and removed, the proxyware might still be running quietly in the background. Expanding to Docker and Brute Force AttacksBesides Magento, the hackers also look for public Docker servers that don’t have security settings in place. They launch new containers inside these servers, downloading and running harmful software. This malware is written in Go (a powerful programming language), and it does many things: Stays active on the system Reads and writes files Runs hidden programs Installs other hacking tools like GSocket and IPRoyal Tries to hack more systems by guessing weak SSH passwords This shows the group’s goal is not just to break into one site but to build a network of infected systems for ongoing income. What This MeansBusinesses running online stores or hosting apps must pay attention. Leaving server settings open or using outdated software is like inviting hackers in. Even platforms widely used by Nigerian tech startups, e-commerce shops, and developers are at risk if they don’t keep their software updated and use strong security measures. By turning hacked computers into mining machines and internet resellers, these attackers are quietly making money off innocent users — often without anyone knowing for weeks or months. To stay safe: Always update your CMS, plugins, and server tools Close unused ports and services Monitor for unknown processes or changes to system files Use tools that can detect in-memory threats and hidden malware As attackers continue to grow in skill and boldness, it’s more important than ever to build strong digital defenses — especially if your platform is part of Nigeria’s growing tech and business ecosystem.
-
New Malware Tricks Windows Features to Steal Bank Login Details
🛡️ New Malware Tricks Windows Features to Steal Bank Login DetailsA dangerous computer virus is now using a clever trick on Windows computers to steal people's bank login details. This malware, which researchers are calling Coyote, is specifically targeting users in Brazil but could be a warning for other countries too, including Nigeria. This virus uses a special part of Windows called UI Automation. Normally, this tool helps people with disabilities by allowing screen readers and other programs to access buttons and text in apps. But hackers have now found a way to use this same tool to spy on what you do on your screen — especially when you’re trying to log into your bank or crypto account. What Does the Coyote Malware Do?Once the malware is inside your computer, it starts watching which apps and websites you’re using. It checks if you’re visiting a bank or cryptocurrency site — there are at least 75 banks and exchanges on its target list. If it detects one, it can read the screen and steal your login information. It does this by: Reading what window is active on your screen Looking through the small pieces (called UI elements) inside that window — like buttons, tabs, or address bars Comparing what it finds with a list of targeted financial websites Stealing your login credentials if there’s a match This method is similar to what many Android banking viruses do. They also use “accessibility” features to read and control the screen in the background. Why This MattersThis malware shows that even safe and helpful features in Windows can be misused by attackers. UI Automation was not made for hacking, but it can still be turned into a spying tool if the attacker knows what they’re doing. Unlike older types of malware that might need internet access to function, Coyote can work offline or online, making it harder to stop. What You Can Do to Stay SafeDon’t download unknown software or files Use strong antivirus and keep it updated Monitor your bank and crypto accounts regularly Keep Windows and other programs updated Be careful of suspicious links or attachments, even if they come from someone you know Cybersecurity experts are warning that tricks like this could spread beyond Brazil. As internet banking grows in Nigeria, threats like Coyote could show up locally too. Stay informed. Stay secure.
-
Google Introduces New Tool to Make Open-Source Software More Secure
Google Introduces New Tool to Make Open-Source Software More SecureGoogle has started a new project that will help protect open-source software from hackers who try to sneak harmful code into popular packages used by developers. The project is called OSS Rebuild, and it's meant to stop software supply chain attacks before they reach millions of users. Open-source software (OSS) is used everywhere—from mobile apps to websites, to government platforms. Developers often rely on public package libraries like npm (for JavaScript), PyPI (for Python), and Crates.io (for Rust). These libraries host thousands of free tools that programmers can easily add to their projects. But there's a big problem: some attackers try to upload fake or modified versions of these packages, hiding harmful code inside. If a developer unknowingly uses one of these bad packages, the entire app or website could be at risk. That’s where OSS Rebuild comes in. Google's new system checks the software packages and tries to rebuild them from scratch. If the rebuilt version doesn't match the original, something might be wrong—maybe someone added hidden code. This helps security teams know which packages they can trust and which ones need a closer look. The tool also helps with: Verifying where a software package comes from Making sure the code hasn't been changed by a hacker Helping companies respond faster when a new vulnerability is found Making software more transparent and trusted If a package can't be rebuilt automatically, Google provides a way to build it manually while still checking it for any suspicious changes. With tools like OSS Rebuild, Google hopes to make open-source software much safer for everyone—especially for developers and companies that depend on free tools to build their apps and services.
-
How Hackers Are Exploiting SysAid Software Vulnerabilities to Break into IT Systems
How Hackers Are Exploiting SysAid Software Vulnerabilities to Break into IT SystemsSecurity researchers have discovered that attackers are actively targeting weaknesses in a popular IT service management platform called SysAid. These weaknesses, known as XML External Entity (XXE) vulnerabilities, were found in key components of the software and could allow hackers to gain full control of affected systems. SysAid is used by many businesses and organizations to manage help desk tickets, monitor system health, and automate IT tasks. Because it is often integrated deeply into internal systems, any security flaws in this software can be extremely dangerous. The newly discovered vulnerabilities are related to how SysAid handles XML data. XML is a format used by many applications to send and receive information, and if not handled properly, it can be used to trick the system into giving away sensitive information or executing unauthorized commands. In this case, attackers can send specially crafted XML files that allow them to read private files on the system or even take full control of the application. What makes the situation worse is that these flaws do not require a valid username or password to exploit. That means an attacker can launch an attack remotely without needing to log in. If successful, they could gain administrative access and start moving through other parts of the company’s internal network. One of the most serious risks is that these vulnerabilities can be used together with older issues in the same platform. For example, a previously discovered command injection flaw in SysAid can be combined with the new vulnerabilities to run remote code on the server. In simpler terms, it means an attacker could take over the entire system just by sending some malicious data to the right place. Security researchers at watchTowr Labs first uncovered these flaws earlier this year and notified the company. SysAid responded by releasing a patched version of the software, but not all organizations have updated to the latest release. That has created an opportunity for hackers who scan the internet for unpatched systems. Government agencies and cybersecurity experts are urging companies to update their SysAid software immediately. The patched version not only fixes the new vulnerabilities but also addresses other known security issues. Organizations are also advised to monitor their servers for any suspicious behavior, such as strange XML requests or unexpected logins. Even though SysAid is just one platform, this incident highlights the bigger issue of how small configuration errors or overlooked updates can become major security risks. Hackers are constantly watching for any weakness they can use to get inside a network, and outdated software gives them an easy way in. This is a reminder that keeping software up to date is not just a recommendation — it's a critical part of defending against cyber threats. Organizations that rely on SysAid or similar tools should take a closer look at their current setup and make sure they are not leaving the door open for attackers.
-
How Hackers Are Exploiting SysAid Software Vulnerabilities to Break into IT Systems
How Hackers Are Exploiting SysAid Software Vulnerabilities to Break into IT SystemsSecurity researchers have discovered that attackers are actively targeting weaknesses in a popular IT service management platform called SysAid. These weaknesses, known as XML External Entity (XXE) vulnerabilities, were found in key components of the software and could allow hackers to gain full control of affected systems. SysAid is used by many businesses and organizations to manage help desk tickets, monitor system health, and automate IT tasks. Because it is often integrated deeply into internal systems, any security flaws in this software can be extremely dangerous. The newly discovered vulnerabilities are related to how SysAid handles XML data. XML is a format used by many applications to send and receive information, and if not handled properly, it can be used to trick the system into giving away sensitive information or executing unauthorized commands. In this case, attackers can send specially crafted XML files that allow them to read private files on the system or even take full control of the application. What makes the situation worse is that these flaws do not require a valid username or password to exploit. That means an attacker can launch an attack remotely without needing to log in. If successful, they could gain administrative access and start moving through other parts of the company’s internal network. One of the most serious risks is that these vulnerabilities can be used together with older issues in the same platform. For example, a previously discovered command injection flaw in SysAid can be combined with the new vulnerabilities to run remote code on the server. In simpler terms, it means an attacker could take over the entire system just by sending some malicious data to the right place. Security researchers at watchTowr Labs first uncovered these flaws earlier this year and notified the company. SysAid responded by releasing a patched version of the software, but not all organizations have updated to the latest release. That has created an opportunity for hackers who scan the internet for unpatched systems. Government agencies and cybersecurity experts are urging companies to update their SysAid software immediately. The patched version not only fixes the new vulnerabilities but also addresses other known security issues. Organizations are also advised to monitor their servers for any suspicious behavior, such as strange XML requests or unexpected logins. Even though SysAid is just one platform, this incident highlights the bigger issue of how small configuration errors or overlooked updates can become major security risks. Hackers are constantly watching for any weakness they can use to get inside a network, and outdated software gives them an easy way in. This is a reminder that keeping software up to date is not just a recommendation — it's a critical part of defending against cyber threats. Organizations that rely on SysAid or similar tools should take a closer look at their current setup and make sure they are not leaving the door open for attackers.
-
Hackers Are Stealing Passwords and Taking Remote Control Using Free Tools
Hackers Are Stealing Passwords and Taking Remote Control Using Free Tools — What’s Happening and How They’re Doing ItIn the past few months, cybersecurity experts have noticed a sharp increase in attacks where hackers steal usernames and passwords, and then take control of people’s or companies’ computers — all without needing fancy or expensive malware. Most of these attacks are happening in Mexico and other parts of Latin America, and they are being carried out by a group called Greedy Sponge. These hackers are after money, and they’re going after all kinds of businesses — from banks to shops to farms. Hackers Send Fake Files to Trick VictimsThe hackers usually start their attack by sending a fake ZIP file (a compressed folder), which may look like a regular update or document. This file often contains: A real-looking file (like a browser or software installer) A hidden virus that installs itself quietly in the background Once someone opens this ZIP file and clicks inside, the virus gets installed and starts its work without them knowing. What the Virus Does: AllaKore RATThe main tool hackers are using is called AllaKore RAT. RAT stands for Remote Access Trojan — basically, a tool that lets hackers take full control of your computer from far away. With AllaKore RAT, hackers can: Log your keystrokes (see what you type, including passwords) Take screenshots Upload or download files Use your computer like it’s their own In short, they can spy on you or steal sensitive information like bank logins and business documents. Smart Tricks to Hide Their ActivityThese hackers are not super advanced, but they’re smart. They’ve changed the way their tools work so that: Only people in Mexico (or certain locations) can download the full virus — this makes it harder for security teams outside the region to study it. The fake software they send looks exactly like real tools, so victims trust it. The virus can also install other harmful tools later, like: SystemBC – Turns your computer into a secret gateway for hackers Ghost Crypt – Helps viruses hide from antivirus programs like Microsoft Defender Hijack Loader – Used to sneak in even more dangerous malware like RedLine Stealer Some Hackers Even Call Victims to Speed Things UpIn one recent attack, hackers pretended to be a new client, sent a fake PDF file, and even called the victim to rush them into opening the file and installing the virus. This method is called social engineering — using human tricks instead of code. New Tools Like Neptune RAT and PureRATOther hackers are using new versions of tools like: Neptune RAT (used to take screenshots, log keystrokes, steal data) PureRAT (similar to AllaKore, also used for spying) XWorm (which Neptune is partly based on) These tools are easy to find and can be used by even low-skill hackers, making them popular for cybercrime. How Do These Tools Bypass Security?Hackers are using tools like: Ghost Crypt – A special service that hides viruses inside other files so they look safe Inno Setup Loaders – These are fake installers that sneak malware into your system when you think you're installing normal software For example, one type called Hijack Loader installs RedLine Stealer, which is made to steal saved passwords, browser data, and more. Why They’re Doing This: It’s All About the MoneyMost of these attacks are not meant to cause destruction — they’re meant to steal information that can be sold or used to access bank accounts, payment systems, or business platforms. Once hackers get in, they can: Sell your login info on hacker forums Access your bank account or online tools Use your PC to attack other people What You Can Do to Stay SafeEven if you’re not in Mexico or Latin America, these attacks can happen anywhere. Here’s how to protect yourself: Never open ZIP files from unknown senders Use antivirus software and keep it updated Use strong, unique passwords (and never reuse the same one) Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible Be suspicious of urgent requests, especially if someone calls or emails you asking to open a file Hackers don’t need advanced tools anymore. With free remote-access tools and simple social engineering tricks, they’re stealing credentials and running attacks on real companies every day. Stay alert, be cautious with email attachments, and always question what you're downloading or clicking. If you work in a business — especially in finance, retail, or public services — share this with your team. Most attacks start with one person clicking the wrong thing.
-
How Hackers Are Breaking Into Big Retail Brands Without Using Malware — And What You Can Learn From It
How Hackers Are Breaking Into Big Retail Brands Without Using Malware — And What You Can Learn From ItIn the past year, some of the world’s most well-known retail brands have fallen victim to cyber attacks. These include Adidas, The North Face, Cartier, Victoria’s Secret, Marks & Spencer, Co-op, and even Dior. What’s shocking is that these attacks didn’t involve high-end malware or advanced hacking tools. Instead, they were identity-based attacks — a growing method where hackers don’t break in. They log in using real usernames, passwords, and system access that wasn’t protected properly. These attacks happened because of poor identity management, over-trusted third parties, unused admin accounts, and weak access controls in cloud-based services. And because they relied on real credentials and legitimate sessions, they often went unnoticed for a long time. Let’s look deeper into what happened, how these attacks worked, and how any business — even smaller retailers — can learn from them to protect themselves. 1. Adidas: Trusting the Wrong Third Party Can Open the DoorAdidas didn’t get hacked directly. The breach happened through a third-party vendor they hired for customer service. That vendor got attacked, and as a result, customer data was exposed — including names, emails, and order information. The issue here wasn’t malware. It was too much access given to a third party, and that access wasn’t taken away after it was no longer needed. This kind of situation is often called a supply chain attack. Why this matters: Many companies allow vendors or partners to connect their tools and software using tokens or service accounts. These connections are rarely monitored, and they often don’t expire or require multi-factor authentication (MFA). That makes them easy targets for hackers looking for quiet, hidden ways into your system. What to take away: Don’t just protect your employees. Review and manage what third-party systems and vendors have access to your data, and turn off those access points when they’re no longer needed. 2. The North Face: When Password Reuse and No MFA Lead to TroubleThe North Face suffered a credential stuffing attack — which is when attackers try usernames and passwords leaked from other websites to log into customer accounts. No malware. No phishing. Just weak password habits, reused credentials, and the absence of MFA. Once inside, attackers quietly accessed personal information. Why this matters: This was not the first time The North Face was hit by a credential attack. In fact, it was their fourth incident like this since 2020. Many SaaS platforms still don’t enforce MFA, and users often reuse the same password across multiple accounts. What to take away: Credential stuffing is still one of the easiest ways for attackers to get in. Every account — especially those connected to SaaS platforms — needs MFA, strong password policies, and protections against multiple failed login attempts. 3. Marks & Spencer and Co-op: Social Engineering Beats TechnologyThese UK retailers were targeted by a group called Scattered Spider. The attackers used SIM swapping and social engineering to impersonate employees. Then, they called the IT help desks and tricked staff into resetting passwords and MFA settings — giving attackers full access. No malware, no phishing emails. Just smart social manipulation. Why this matters: Attackers know that humans are the weakest link. Even strong security tools can’t stop an employee from being tricked. Once inside, attackers often go after admin-level accounts or service accounts that no one monitors. What to take away: Help desk staff need better training to spot social engineering attempts. Security policies should prevent help desk staff from resetting passwords or MFA unless strict verification steps are met. And access to sensitive SaaS tools should always be limited and logged. 4. Victoria’s Secret: When SaaS Admin Accounts Go UnwatchedVictoria’s Secret had to delay its earnings report due to a cyber incident that affected both their website and in-store systems. While technical details were not made public, signs point to the breach coming from within their SaaS platforms — likely from an overprivileged admin account that wasn’t protected properly. Why this matters: Many SaaS applications (like those used for managing inventory, processing orders, or handling analytics) rely on internal admin roles. If those roles are misconfigured, or if an attacker takes control of them, the damage can be massive. It doesn’t even require malware — just legitimate access. What to take away: Admin accounts should be closely monitored, and access permissions should be reviewed regularly. Just because someone is an admin today doesn’t mean they still need to be one next quarter. 5. Cartier & Dior: Customer Support Platforms Can Be a Hidden WeaknessCartier and Dior were breached through the SaaS platforms they used for customer service and CRM (Customer Relationship Management). Attackers didn’t go through their internal systems — they targeted external platforms used to help customers. These platforms are often connected to internal systems using API keys or machine accounts that rarely rotate and are easy to forget about. Why this matters: Customer service tools may seem harmless, but they often hold sensitive customer information — and they’re frequently connected to back-end systems. If those non-human accounts aren’t protected, hackers can steal massive amounts of data. What to take away: Every SaaS platform connected to your business is part of your attack surface. You should track how customer data flows through these systems and make sure all integrations are secure, especially those using API tokens or service accounts. So, What’s the Bigger Picture Here?What all these incidents show is that you don’t need fancy malware or complex exploits to breach a major company. Hackers are getting in by using what's already available — usernames, forgotten tokens, weak passwords, and human mistakes. They’re exploiting: Third-party vendors who still have access Passwords reused across different platforms Help desk staff tricked into handing over access Overprivileged SaaS admin accounts Machine identities no one monitors These identity-based attacks leave no malware, no digital fingerprints, and very few alerts. That’s why they’re so dangerous — and why more and more attackers are using them. What Can You Do to Protect Your Business?Whether you’re running a global retail chain or a small e-commerce store, you can take real steps to stop these types of attacks. Here are some security tips every organization should follow: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) everywhere — not just for users, but also for service accounts and integrations. Review third-party access regularly. If a vendor no longer works with you, revoke their access immediately. Rotate API keys and tokens periodically. Avoid leaving them active forever. Train your support and help desk staff to recognize social engineering attempts. Limit admin privileges to only those who absolutely need it — and only for as long as they need it. Monitor SaaS identity behavior — both human and machine accounts — and flag anything unusual. Cyber attackers are no longer kicking in the front door. They’re walking in through the side gate, wearing a uniform and holding a key you gave them two years ago. If you're not keeping track of who has access to what, when, and how — you're already at risk. Make identity a core part of your security strategy. Because in today’s world, your weakest point might not be a broken system — it might be a forgotten login.
-
How Hackers Use Free Tools to Attack Banks in Africa — What You Need to Know
Cybersecurity experts have discovered a wave of cyber attacks targeting banks and financial institutions in different parts of Africa. These attacks have been happening since at least July 2023. What’s surprising is that the hackers are not using expensive or custom-made tools. Instead, they are using open-source tools — tools that anyone can download for free from the internet. These hackers are smart. They use tricks to hide what they’re doing and make it look like they’re running normal programs. They even copy the signatures and icons of trusted software like Microsoft Teams or Palo Alto Cortex, so it’s harder for security systems to catch them. A cybersecurity research group called Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 is keeping track of this cybercrime activity. They’ve named it CL-CRI-1014 — “CL” stands for “cluster” and “CRI” stands for “criminal.” They believe the hackers’ goal is to break into computer systems and then sell that access to other criminals on the dark web. These types of hackers are known as Initial Access Brokers (IABs). What Tools Are the Hackers Using?These cybercriminals are using a mix of free, open-source software tools, including: PoshC2 – a tool used for controlling infected computers remotely. Chisel – a tool that allows hackers to secretly send information in and out of a network. Classroom Spy – a remote access tool originally meant for teachers to monitor students, but now being misused. Once they get into a network, the attackers usually install these tools to take over systems, move to other devices in the same network, and avoid being detected. How Do They Break In?So far, experts don’t know the exact method the hackers are using to get inside these financial systems. But once they’re in, the attackers install other programs like: MeshCentral Agent – used to control the computer remotely. Classroom Spy – to watch everything users are doing. Chisel – to go around firewalls and security blocks. They also use PoshC2 and make it look like it's part of popular software so that no one suspects anything. To stay inside the system for a long time, they make PoshC2 run automatically using different methods like: Creating a new system service Placing a shortcut in the Windows startup folder Scheduling a fake system task called “Palo Alto Cortex Services” They may also steal usernames and passwords, and use those to create a proxy, which lets them stay hidden and keep communicating with their command-and-control server. Why Is This Important?If you work in the banking or finance sector in Africa — or even run a small business — this is very important. Hackers don’t always go after big companies. They often look for smaller targets that don’t have strong cybersecurity. If they break into your network, they could steal sensitive information or sell access to others who might install ransomware or steal money. This isn’t the first time tools like PoshC2 have been used in Africa. In 2022, a similar attack campaign called DangerousSavanna targeted banks in Ivory Coast, Cameroon, Senegal, Togo, and Morocco. That time, hackers used email phishing to trick people into downloading malware. What Else Is Happening in Cybersecurity?In addition to these attacks in Africa, another threat is growing worldwide. A new ransomware group called Dire Wolf has recently attacked at least 16 companies in the U.S., India, Australia, Canada, and other countries. Their favorite targets include: Technology companies Manufacturing companies Financial services The Dire Wolf ransomware is built using a language called Golang, and it can do serious damage. It can: Stop important system logs (making it harder to trace the attack) Shut down over 75 services and 59 programs Delete backup copies of data so victims can't recover While we don’t yet know how Dire Wolf gets into systems, companies are being advised to monitor their systems carefully and follow best practices like using strong passwords, keeping software updated, and training employees on phishing attacks. How Can You Protect Your Business?If you own a website, run a business, or manage a bank or fintech company in Africa, here are some important things you should do: Use strong and unique passwords for all systems Install antivirus software and keep it up to date Educate your employees about phishing emails and fake downloads Update your software and operating systems regularly Use a firewall and intrusion detection system Monitor your network for strange behavior Use two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible Also, avoid downloading unknown software and be cautious of attachments or links in emails, even if they look like they came from someone you trust. Cybercrime is growing quickly, and hackers are getting smarter every day. By learning how these attacks work and how to protect yourself, you can help keep your company and customers safe. Cybersecurity is not just for IT teams anymore. Everyone — from employees to small business owners — must take part in keeping systems secure.
-
UK Cybercrime Crackdown: Four Suspects Arrested Over Massive Attacks on Major Retailers
The UK’s National Crime Agency (NCA) has announced the arrest of four individuals in connection with large-scale cyber attacks that caused significant financial damage to some of the country's most recognized retail brands. The attacks, which reportedly targeted Marks & Spencer, Co-op, and Harrods, are estimated to have caused losses of up to £440 million. The individuals arrested include three young men aged 17, 19, and 19, along with a 20-year-old woman, all apprehended in coordinated operations across London and the West Midlands. Authorities confirmed that these arrests are part of an ongoing investigation into organized cybercrime, focusing on breaches that leveraged ransomware and social engineering to gain unauthorized access to corporate systems. The Scale and Nature of the AttacksAccording to the Cyber Monitoring Centre (CMC), the cyber operations were classified as a single, coordinated cyber event, rather than unrelated breaches. The total financial impact is believed to be between £270 million and £440 million, representing one of the most damaging cyber incidents targeting UK retailers in recent years. The nature of the attack suggests a high level of planning and coordination. Marks & Spencer, during a parliamentary hearing earlier this month, confirmed that their systems had been impacted by ransomware, specifically naming a group known as DragonForce. Investigators believe DragonForce did not act alone, but rather operated in collaboration with other loosely affiliated actors forming part of a broader cybercriminal ecosystem. Suspected Link to Scattered SpiderWhile the NCA has not publicly confirmed the names of the groups behind the attacks, investigators and private sector experts believe that elements of the cyber campaign may be connected to a notorious hacking collective known as Scattered Spider. This decentralized cybercrime group has made a name for itself through its use of advanced social engineering techniques to breach organizations and deploy ransomware. Unlike traditional financially-motivated groups that rely heavily on malware alone, Scattered Spider has gained notoriety for leveraging human manipulation—voice phishing, impersonation of employees, and infiltration of help desk systems—to gain access to corporate networks. Security analysts have described the group as one of the most persistent and capable adversaries targeting Western organizations. Scattered Spider is believed to be an offshoot of a broader loose-knit collective known as The Com, which has been linked to a range of illegal activities beyond cybercrime, including sextortion, SIM swapping, swatting, and even violent crimes such as kidnapping and murder. This blending of traditional cybercrime with broader criminal behavior underscores the evolving threat landscape organizations now face. Arrests a Major Step Forward, but Investigation ContinuesDeputy Director Paul Foster, who leads the National Cyber Crime Unit at the NCA, called the arrests a major development in a complex, fast-moving investigation. According to Foster, “These arrests represent significant progress, but our work continues alongside international partners to identify all individuals involved and hold them accountable.” The four suspects were arrested at their residences, and authorities have seized electronic devices for forensic examination. Investigators are expected to analyze digital evidence for connections to known threat groups, stolen data, ransom negotiation records, and cryptocurrency transactions. Notably, independent cybersecurity researcher Brian Krebs later identified two of the suspects as Owen David Flowers and Thalha Jubair, both of whom are allegedly linked to earlier cybercriminal operations. Jubair, in particular, is suspected of having been a key member of the LAPSUS$ group and the former administrator of Doxbin, a pastebin platform used for publishing personal data. A Profile of the Modern AttackerWhat sets Scattered Spider apart from traditional cybercriminal groups is not only their tactics, but also their demographic makeup. Unlike many groups based in Eastern Europe or Asia, Scattered Spider is believed to consist largely of young, native English speakers. This gives them an edge in voice-based social engineering attacks, as they can convincingly impersonate employees during phone calls to IT help desks or customer support centers. Security experts warn that many of these individuals are teenagers, lured into cybercrime by promises of quick financial rewards, often without fully understanding the legal consequences. Some begin participating in phishing operations and vishing calls while still underage, a trend that law enforcement has started to clamp down on more aggressively. Threat researcher Zach Edwards noted that these young actors are being used as frontline operatives, making phishing calls and handling initial access operations. Their voices and digital footprints make them easier to track and prosecute, while higher-ranking members of the group remain in the shadows. Tactics and TechniquesReports from cybersecurity firms such as Mandiant and Halcyon provide additional insight into the tools and strategies used by these attackers. One common approach involves creating fake login portals that mimic legitimate corporate systems. Employees are tricked into entering their credentials, which are then captured and used to gain network access. Once inside, attackers often move laterally across the network, deploy ransomware, and extract sensitive data for extortion. In several cases, organizations have been forced into lengthy downtime and expensive recovery processes, not to mention regulatory scrutiny and reputational damage. Defending Against Social Engineering and RansomwareWhile the arrests are a positive sign of law enforcement effectiveness, security professionals caution that the threat has not been eliminated. The decentralized nature of these groups means others may quickly take their place. Organizations must use this window of opportunity to strengthen their defenses. Some key defensive recommendations include: Training help desk staff to enforce strong identity verification protocols Deploying phishing-resistant Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) across all accounts Monitoring for suspicious domains and fake login pages mimicking corporate portals Keeping incident response plans up to date and tested regularly Collaborating with threat intelligence providers to stay informed on emerging attack techniques Charles Carmakal, CTO at Mandiant Consulting, described the arrests as “a significant win” but emphasized the importance of international collaboration and proactive defense. According to Carmakal, the effectiveness of groups like Scattered Spider is not due to novel techniques, but their persistence and skill in manipulating human trust. The Bigger PictureThis case highlights the changing nature of cybercrime in 2025. Cybercriminals are becoming younger, more organized, and more audacious in their methods. As the lines between digital and physical crimes continue to blur, law enforcement agencies must adapt quickly—and businesses must take security more seriously than ever before. While arrests bring temporary disruption, the long-term solution lies in security awareness, technological preparedness, and cross-border law enforcement cooperation. Organizations, especially those in retail, finance, and healthcare, must not wait for a breach to take action. The tools and techniques used in these recent attacks are widely available, and many criminal groups now operate with professional structures, financial incentives, and even recruitment pipelines that target tech-savvy youth. Taking cybersecurity seriously is no longer optional—it is a business imperative.
-
Chinese Cyber Espionage Groups Exploit SharePoint Vulnerabilities in Coordinated Attacks, Microsoft Warns
Chinese Cyber Espionage Groups Exploit SharePoint Vulnerabilities in Coordinated Attacks, Microsoft WarnsMicrosoft has issued a new warning about a series of active cyberattacks targeting vulnerable SharePoint Server systems. These attacks have been formally linked to multiple Chinese state-sponsored threat actors, highlighting an urgent security risk to organizations still running unpatched, internet-facing SharePoint deployments. The tech giant confirmed that three advanced persistent threat (APT) groups—Linen Typhoon, Violet Typhoon, and Storm-2603—have been exploiting previously identified vulnerabilities in SharePoint servers, using them as a stepping stone to gain unauthorized access to enterprise networks. According to Microsoft, the malicious activity has been ongoing at least since July 7, 2025, and appears to be increasing in scope and sophistication. The company’s latest intelligence also aligns with earlier reports from other cybersecurity firms, reinforcing the seriousness of the campaign. SharePoint Flaws Being ExploitedAt the core of the attacks are vulnerabilities in on-premises SharePoint Server environments, including: CVE-2025-49706 – a spoofing vulnerability CVE-2025-49704 – a remote code execution (RCE) flaw While Microsoft previously released patches for these issues, the threat actors have found workarounds that bypass the original fixes. These bypass methods have now been assigned new identifiers: CVE-2025-53771 CVE-2025-53770 In real-world exploitation observed by Microsoft, attackers are targeting the SharePoint ToolPane endpoint using crafted POST requests. This method allows them to bypass authentication mechanisms and execute code remotely on the server. From there, attackers typically deploy a web shell—usually named spinstall0.aspx, spinstall1.aspx, or similar—giving them persistent backdoor access to the compromised environment. This web shell provides access to sensitive server-side data, including MachineKey information, which can be used to facilitate lateral movement, further exploitation, or data theft. Groups Behind the ExploitationLinen TyphoonAlso known as APT27, Bronze Union, Lucky Mouse, or Emissary Panda, this group has been active since at least 2012. Known for their use of tools like SysUpdate, HyperBro, and PlugX, Linen Typhoon has a long history of conducting cyber espionage campaigns targeting both private and government-sector networks. Violet TyphoonActive since around 2015, Violet Typhoon is also known as APT31 or Zirconium. The group has previously conducted campaigns against countries including the United States, Finland, and Czechia. They are known for targeting sensitive geopolitical and technology-related sectors. Storm-2603A newer China-based actor, Storm-2603 is believed to have ties to the deployment of both Warlock and LockBit ransomware. While not as well-documented as the other two groups, Microsoft’s report suggests that Storm-2603 has become increasingly active in exploiting unpatched SharePoint vulnerabilities as part of its initial access strategy. Deeper Technical Analysis Reveals Sophisticated BehaviorCybersecurity researcher Rakesh Krishnan contributed additional insights into the tactics being used during forensic analysis of these attacks. In at least one case, investigators found that the exploitation process involved three different invocations of Microsoft Edge, including: Network Utility Process Crashpad Handler GPU Process Each of these processes has a legitimate role in the Chromium browser architecture. However, the attackers are believed to have used them strategically to mimic typical system behavior and evade sandbox detection tools. Even more alarming, the malicious web shell used by the attackers was found to communicate using Google’s Client Update Protocol (CUP). By doing so, the attackers are able to disguise their traffic as routine browser update checks, making it far more difficult for defenders to detect or block the communication. Recommended Mitigations for OrganizationsIn response to the threats, Microsoft has published a set of urgent mitigation recommendations. Organizations using SharePoint Server Subscription Edition, SharePoint Server 2019, or SharePoint Server 2016 should take the following actions without delay: Apply all recent SharePoint updates, including patches that address CVE-2025-53770 and CVE-2025-53771. Rotate ASP.NET machine keys used by the SharePoint instance to prevent reuse by attackers. Restart Internet Information Services (IIS) to ensure any exploited sessions are terminated. Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, such as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, or equivalent. Enable AMSI (Antimalware Scan Interface) and configure it to Full Mode for maximum threat visibility. Ensure that Microsoft Defender Antivirus or an equivalent security solution is installed and up to date across all systems. These steps are necessary to reduce exposure and eliminate persistence mechanisms that threat actors may have left behind on compromised servers. History of Chinese Threat Activity Targeting Microsoft ProductsThis is not the first time Microsoft has publicly attributed large-scale cyber campaigns to Chinese state-sponsored groups. In March 2021, a group referred to as Silk Typhoon (formerly known as Hafnium) was linked to the mass exploitation of Microsoft Exchange Servers through a series of zero-day vulnerabilities. That attack, later dubbed ProxyLogon, impacted thousands of organizations globally and became one of the most significant cybersecurity incidents of that year. Adding further context to China's cyber activities, earlier in July 2025, a 33-year-old Chinese national named Xu Zewei was arrested in Italy. He was charged with conducting cyber attacks against U.S. organizations and government agencies, specifically using the same Exchange Server vulnerabilities exploited during the ProxyLogon incident. Outlook and Ongoing ThreatMicrosoft’s assessment of the current situation is blunt: attackers will likely continue to exploit these SharePoint vulnerabilities, especially against unpatched on-premises systems. Organizations that have not yet applied the latest updates or taken other necessary security steps are at significant risk of compromise. As SharePoint remains a widely used platform for internal collaboration, project management, and enterprise content hosting, it presents a highly attractive target for espionage-focused actors. The use of sophisticated tools and techniques—such as encrypted communication, process mimicry, and web shell obfuscation—demonstrates a high level of planning and technical skill. Security teams must treat this campaign as active and ongoing. The window for easy exploitation remains open for any organization lagging behind on updates or operating without modern security monitoring. Final Thoughts on Securing SharePoint EnvironmentsThis recent campaign highlights a broader trend in cybersecurity: attackers are quick to adapt, reuse, and evolve their methods, especially when targeting widely deployed enterprise platforms like SharePoint. Once a vulnerability becomes public—especially one involving authentication bypass or remote code execution—threat actors begin incorporating it into their playbooks almost immediately. As always, staying protected is not about reacting to the breach after it happens, but about preventing it altogether. Keeping your infrastructure updated, actively monitoring systems, and deploying layered security controls can significantly reduce your exposure to these sophisticated threats. For organizations that rely on SharePoint for day-to-day operations, now is the time to act. Apply the latest patches, confirm your security configurations, and work with your IT and cybersecurity teams to close any remaining gaps. Cybersecurity is not a one-time fix—it’s a continuous process of awareness, assessment, and action.
-
How to Install an SSL Certificate on Hostinger to Secure Your Website
How to Install an SSL Certificate on Hostinger to Secure Your WebsiteEvery website on the internet today needs to be secure, whether it's a blog, an online store, a company page, or a portfolio. One of the most basic and important ways to secure your website is by installing an SSL certificate. If your website is hosted with Hostinger, the process of getting and installing an SSL certificate is straightforward, and most importantly, it can be done for free. In this blog post, you will learn what SSL is, why you need it, how it works, and how you can install an SSL certificate on your website using Hostinger. This guide is written for beginners, so you do not need any technical experience to follow along. You just need access to your Hostinger account and your domain name. What is SSL and Why is It Important?SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It is a digital security technology that creates a secure connection between a web server (where your website is hosted) and a web browser (like Chrome or Firefox). When someone visits your site and it has an SSL certificate installed, their connection is encrypted. That means no one else can see what information is being sent or received. This is especially important if your website collects any kind of personal data from users. For example, login details, email addresses, or payment information. Without SSL, all of that data is sent in plain text and can be intercepted by attackers. SSL makes sure that only the person who is supposed to receive the data can see it. Besides security, SSL also impacts trust and SEO. When your site has SSL, the browser shows a padlock symbol and the address of your site begins with "https" instead of just "http". Visitors feel safer when they see this. Also, search engines like Google favor secure websites. That means installing SSL can help your site rank better in search results. Does Hostinger Provide Free SSL?Yes, Hostinger provides free SSL certificates with most of its hosting plans. If you have purchased a shared hosting, WordPress hosting, or cloud hosting plan from Hostinger, you will likely have a free SSL option already included. If you are not sure, you can check your account dashboard or contact Hostinger support. Even if your hosting plan does not include free SSL, Hostinger allows you to manually install an SSL certificate obtained from services like Let’s Encrypt. But for most users, the built-in SSL service is more than enough. How to Check if Your Website Has SSL AlreadyBefore installing a new SSL certificate, you should check if your site already has one. The easiest way to do this is by visiting your domain in a browser. If the address starts with “https://” and the browser shows a secure padlock, then you are already using SSL. If it says “Not Secure” or the address only shows “http://”, then SSL is not installed or not active. You can also use tools like SSL Checker (sslshopper.com or whynopadlock.com) to scan your site and confirm the status of your SSL certificate. Installing SSL Certificate on HostingerIf you have confirmed that SSL is not yet active on your website, you can go ahead and install it using the Hostinger control panel, also known as hPanel. You need to log into your Hostinger account and access the hosting management section for the website you want to secure. In your hPanel dashboard, look for the SSL section. Hostinger usually places it under the "Advanced" or "Security" section, but you can also use the search bar to find it faster. Once you are in the SSL area, you will see your domain listed. If SSL is not active, there should be an "Install SSL" or "Activate" button next to the domain name. Clicking this button will begin the installation process. Hostinger handles the technical side of SSL installation automatically. You do not need to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), upload certificate files, or make any server changes manually. Everything is done for you once you click the activation button. The SSL activation process usually takes a few minutes. After that, your site should be accessible using "https" and you can test it to confirm it’s working. How to Force HTTPS on Your WebsiteEven after installing SSL, your website may still load using "http" unless you force it to always use "https". This is a common issue that can confuse visitors and reduce the benefits of having SSL. Hostinger provides a simple setting to fix this. In the same dashboard where you activated SSL, you should find an option called "Force HTTPS" or “HTTPS Redirect.” Enabling this setting ensures that anyone who visits your website using "http" will be automatically redirected to the secure "https" version. This feature is important because it makes sure that every page of your website benefits from encryption. Without this redirect, some pages may load insecurely, which can lead to browser warnings or SEO penalties. What to Do If You Don’t See the SSL OptionIn some cases, especially with older or cheaper hosting plans, you may not see the SSL option in your hPanel. If that happens, the first thing you should do is contact Hostinger support. They are available 24/7 and can check if SSL is available for your plan or help you upgrade to a plan that includes it. Another option is to get a free SSL certificate from a third-party provider like Let’s Encrypt and install it manually. This process is more technical and involves generating certificate files, uploading them to your server, and configuring your web server settings. For beginners, it’s better to use the free SSL option included in Hostinger if available. Additional Things to Check After SSL InstallationAfter you install and activate SSL, it’s a good idea to test your entire website to make sure everything works properly. Here are a few things you can check: Visit your website in different browsers to confirm the secure padlock appears Try visiting both http://yourdomain.com and https://yourdomain.com to make sure it redirects correctly Look through your website pages to check that all content is being loaded over HTTPS Use online tools like Why No Padlock or SSL Labs to run deeper tests If any content on your site is still loading over HTTP (for example, images or scripts), your browser may show a warning like "Mixed Content." You should update those resources to use HTTPS as well. Final Words Securing your website with an SSL certificate is one of the first and most important steps you should take after launching your website. It protects your visitors' data, improves your site’s reputation, and helps you gain better visibility on search engines. If you are using Hostinger as your hosting provider, the process is very simple and user-friendly. You can activate SSL with just a few clicks through the Hostinger control panel. There is no need for technical knowledge or extra tools. Always make sure you also enable HTTPS redirection so that all your traffic is protected. Once your SSL certificate is live and working, your site will be safer, faster, and more trustworthy to every visitor. If you are planning to start an online business or collect any kind of user data, having a secure connection is not optional anymore—it is required. And with hosting providers like Hostinger making it easier than ever, there is no reason not to do it today. By following this guide, you now know what SSL is, why it matters, and how to install it quickly and easily using Hostinger. Make sure you keep your website safe and professional, starting with a strong foundation of security through SSL.
-
Python for Beginners: Giving Instructions to the Computer
👨💻 Python for Beginners: Giving Instructions to the Computer When you write a Python program, you're simply telling the computer what to do — step by step 🪜. Python reads each line from top to bottom 📖 and does exactly what you say. Let’s look at some simple examples: 🖨️ 1. Printing a Messageprint("Hello, World!")🧾 What it does: It tells Python to show this text on the screen. 💡 Output: Hello, World!🔢 2. Doing Mathprint(5 + 3)➕ This adds 5 and 3 and prints the result. 💡Output: 8You can also subtract (−), multiply (×), and divide (÷): print(10 - 2) # Subtractionprint(4 * 2) # Multiplicationprint(16 / 4) # Division📦 3. Storing Information in Variablesname = "Aisha"print("Hello, " + name)📌 You stored a name in a variable. Then you used it to print a custom message. 💡 Output: Hello, Aisha✅ 4. Making Decisions (If Statements)age = 18if age >= 18: print("You are an adult!")🤔 The computer checks if the person is 18 or older. 💡 Output: You are an adult!🔁 5. Repeating Things (Loops)for i in range(5): print("Hi!")🔁 This prints "Hi!" five times. 💡 Output: Hi!Hi!Hi!Hi!Hi!🎉 That’s it!Python is easy to read and write. With a few lines, you can already: 📤 Display messages 🧮 Do math 🧊 Store data 🧠 Make decisions 🔁 Repeat tasks Keep practicing, and soon you’ll be writing your own cool programs! 🐍🚀
-
Introduction to Python Programming
🐍 Introduction to Python Programming📌 What is Python Programming?Python programming is a way to tell a computer what to do using the Python language, which is known for being simple and easy to read. 🌐 Why is Python Popular?Python is a popular language that many people use to: Create apps Build websites Develop games And much more! 🧠 What Can You Do with Python?Python allows you to write instructions for the computer to follow. These instructions can help you: Solve math problems Process and analyze data Automate tasks And perform many other functions
-
Melissa Virus – One of the First Email-Based Macro Malware
🦠 Melissa Virus – One of the First Email-Based Macro MalwareThe Melissa Virus was one of the earliest and most widespread examples of macro-based malware. Emerging in March 1999, it quickly became infamous for leveraging Microsoft Word and Outlook to spread rapidly across the internet, causing email servers to slow down or crash due to the volume of infected messages. 📄 What is the Melissa Virus?Melissa is a Microsoft Word macro virus. It arrives as an email attachment, typically named LIST.DOC. When the document is opened in Microsoft Word, the macro code embedded inside it gets executed. The virus modifies Microsoft Outlook to automatically send itself to the first 50 people in the victim’s address book. Despite its rapid spread, Melissa does not destroy data or crash your system. It just manipulates Word settings and propagates itself through email. 📬 How Melissa SpreadsMelissa uses social engineering to trick users into opening the infected file. Here's how the infection process works: 1. Email ReceivedYou receive an email with the following details: Subject: "Important message from [name of someone you know]" Message Body: "Here's the document you asked for...don't show anyone else ;-)" Attachment: LIST.DOC (a Word document containing the malicious macro) 2. User Opens the FileWhen the user double-clicks the file, the macro inside the document runs automatically (if macros are enabled in Word). 3. Outlook Gets CompromisedMelissa accesses Microsoft Outlook and sends the same infected email to the first 50 contacts in the user’s address book — repeating the cycle. ❌ What Does Melissa Do?Does Not: Corrupt your files Delete data Crash your system Does: Modify certain Microsoft Word settings Use your Outlook to email itself to others Spread without your knowledge The biggest danger was spreading sensitive content to unintended recipients, potentially breaching privacy or leaking documents unintentionally. 🛡️ How to Protect Against Macro Viruses Like MelissaDisable Macros: Always disable macros in Microsoft Office unless you absolutely trust the source. Use Antivirus Software: Modern antivirus tools can detect and block macro-based threats. Keep Software Updated: Microsoft has patched many vulnerabilities used by such viruses in later versions. Educate Users: Teach employees and users not to open unexpected attachments, even from known contacts. 🕵️ Historical ImpactMelissa spread to thousands of computers within hours. It caused email servers in large organizations (like Microsoft and the U.S. Marine Corps) to shut down temporarily. The creator, David L. Smith, was eventually caught and sentenced to prison. Melissa was a turning point in the world of malware. It demonstrated how combining social engineering with software macros could cause widespread disruption — all without traditional payloads like file deletion or system crashes. 🧠 Key TakeawayThe Melissa virus may seem harmless compared to modern ransomware or spyware, but it’s a powerful lesson in how user trust and software automation can be exploited. Always be cautious with attachments — even from people you know.
-
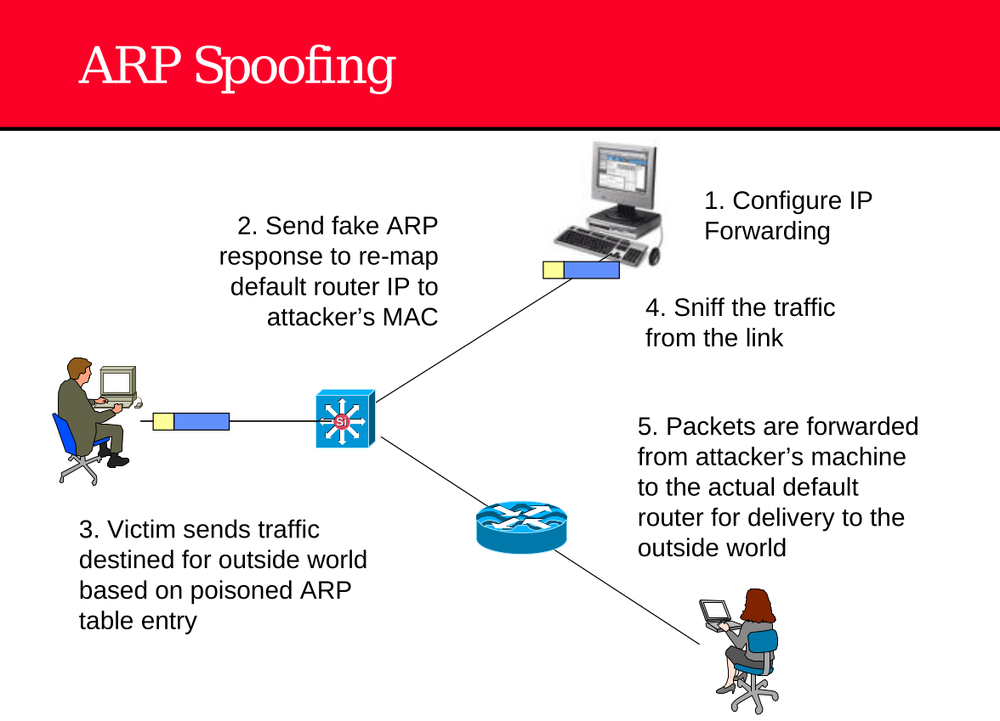
ARP Spoofing (Also known as ARP Poisoning)
🛑 ARP Spoofing (Also known as ARP Poisoning)ARP Spoofing is a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack technique used by attackers on a local network to intercept, modify, or redirect traffic between two devices. It exploits the weaknesses in the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which is used to map IP addresses to MAC addresses on LANs. 🧠 How ARP Works (Briefly)Devices on a LAN use ARP to find the MAC address corresponding to an IP address. For example, a device will send an ARP request like: "Who has IP 192.168.1.1? Tell 192.168.1.100" The router (192.168.1.1) replies with its MAC address, and this is stored in the device’s ARP table. ⚠️ ARP Spoofing Attack Steps (Explained)1. Configure IP Forwarding (Attacker’s Machine)Before launching the attack, the attacker enables IP forwarding on their system. This allows them to pass network traffic between the victim and the real gateway (router), so the connection isn’t broken. echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward2. Send Fake ARP Responses (Spoofing the Router)The attacker sends forged ARP replies to the victim’s machine. These ARP packets falsely claim: As a result, the victim updates its ARP table and associates the router’s IP with the attacker’s MAC address. 3. Victim Sends Internet-Bound Traffic to AttackerThe victim now believes the attacker is the gateway. Any traffic intended for the internet or other external networks is unknowingly sent to the attacker. 4. Sniff the TrafficSince the attacker is now in the middle, they can: Capture usernames, passwords, session cookies Read or alter unencrypted traffic (HTTP, FTP, etc.) Use tools like Wireshark, Ettercap, or Bettercap to monitor or manipulate the data. 5. Forward Packets to Real Router (Avoid Detection)To avoid breaking the network connection and raising suspicion, the attacker forwards the intercepted packets to the real default gateway. This keeps the victim online, making the attack stealthy. So the attacker becomes a transparent proxy, observing everything while passing traffic both ways. 🧰 Tools Used in ARP SpoofingEttercap Bettercap Arpspoof (Dsniff suite) Cain & Abel (Windows) 🛡️ Prevention & DetectionDefense Method Description Static ARP entries Manually assign IP-to-MAC mappings (not scalable). Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) Available on managed switches; blocks ARP spoofing. Use HTTPS Encrypts data so even sniffed traffic is useless. Use VPNs Adds encryption and obfuscates IP data. ARP Watch Tools Detect changes in ARP tables. IDS/IPS Systems Monitor ARP traffic for anomalies. ARP Spoofing is a powerful yet simple attack used to perform man-in-the-middle attacks on local networks. While it doesn’t require much technical skill to launch, it can have severe consequences—especially on networks lacking basic security mechanisms.
-
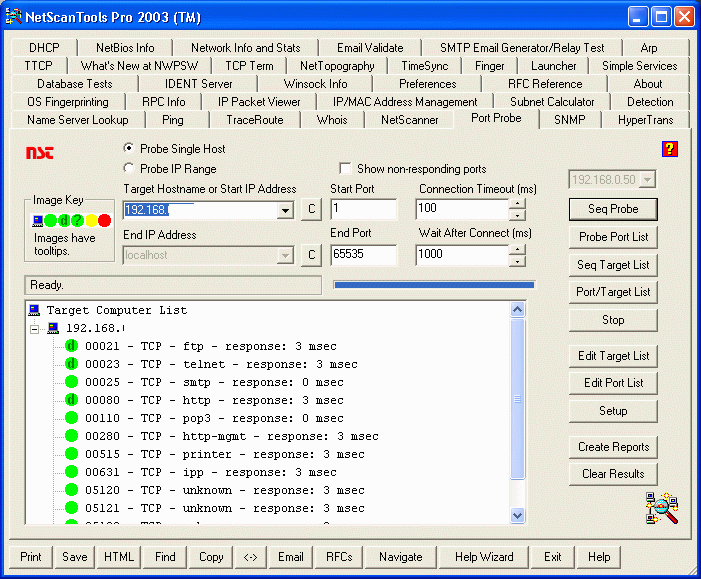
NetScanTools Pro 2003 – A Network Investigation Powerhouse
🧰 NetScanTools Pro 2003 – A Network Investigation PowerhouseNetScanTools Pro 2003 is a powerful and versatile network utility suite developed by Northwest Performance Software, Inc. It was designed primarily for IT professionals, system administrators, and cybersecurity analysts to perform network diagnostics, reconnaissance, and troubleshooting on Windows platforms. Although released in 2003, the tool offered a wide range of features that made it a go-to utility suite for Windows-based network analysis at the time. 🧭 What is NetScanTools Pro?NetScanTools Pro is a standalone software toolkit containing over 40 individual tools that focus on information gathering, testing network services, and analyzing protocols. These tools are both manual and automated, making it useful for both beginners and experts. 🔧 Key Features of NetScanTools Pro 2003Here’s a breakdown of some of the most notable features it offered in 2003: 1. Port ScanningOne of the primary features. Supported both TCP and UDP port scans. Could detect open, closed, and filtered ports. Useful for discovering services running on a target host. 2. Ping and TracerouteBasic connectivity and routing tools. Used ICMP and other packet types. Visual representation of route taken by packets from source to destination. 3. Whois LookupProvided domain registration information. Supported recursive lookups through multiple Whois servers. 4. DNS ToolsQuery various DNS records: A, MX, NS, PTR, etc. Helped in understanding domain resolution and misconfigurations. 5. IP Scanner / Subnet ScannerScan a range of IP addresses in a network. Identify live hosts, open ports, and services. 6. Email ToolsVerified the existence of email addresses via SMTP probing. Helped test open relays or mail server misconfigurations. 7. Time Sync ToolsSynchronize the system clock with NTP servers. Important for time-sensitive logging or coordination across systems. 8. Packet Capture and AnalysisSupported basic packet capture to monitor traffic. Used raw sockets (not as advanced as Wireshark, but useful for quick diagnostics). 9. Automated ToolsSome operations could be scripted or scheduled. Reports could be exported for documentation or auditing purposes. 💼 Use Cases for NetScanTools Pro 2003Network Troubleshooting: Diagnose connectivity issues, check DNS problems, and test service availability. Penetration Testing (Basic): Perform reconnaissance, port scans, and information gathering. System Administration: Routine checks on mail servers, DNS resolution, and uptime tracking. Security Auditing: Identify exposed ports and test the visibility of internal systems to the public network. 🕰️ Historical ImportanceIn the early 2000s, NetScanTools Pro was considered a must-have utility suite for Windows-based network diagnostics, especially before the widespread popularity of open-source tools like Nmap, Wireshark, or Metasploit. While newer versions with updated features were released in later years, the 2003 version marked a major turning point in the tool’s adoption and capabilities. ⚠️ LimitationsOnly available for Windows operating systems. Lacked advanced stealth scanning techniques found in modern tools. No active development of the 2003 version; newer versions are recommended for current systems. 📦 Modern AlternativesWhile NetScanTools Pro is still available today in modern versions, if you're looking for current tools with similar or extended functionality, consider: Nmap/Zenmap Wireshark Advanced IP Scanner Angry IP Scanner Netcat NetScanTools Pro 2003 was a comprehensive suite for its time, offering a range of powerful utilities that made it invaluable to network administrators and security testers. It provided a user-friendly GUI and broad diagnostic capabilities, making it easier for users to understand the underlying behavior of network systems and services.
-
TCP Three-Way Handshake (Explained)
🔁 TCP Three-Way Handshake (Explained)The TCP three-way handshake is the process used to establish a reliable connection between a client and a server over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). It ensures both sides are ready to communicate and agree on starting parameters like sequence numbers. 🔐 Why It's Important:Ensures both client and server are ready for communication. Helps synchronize sequence numbers for reliable data transfer. Prevents half-open or unreliable connections. 🧱 Steps of the Three-Way Handshake1. SYN (Synchronize) — Client → ServerThe client wants to start a connection. It sends a SYN packet to the server. This packet contains an initial sequence number (ISN), which starts the conversation. 📩 Example: Client sends: SYN, SEQ=10002. SYN/ACK (Synchronize/Acknowledge) — Server → ClientThe server receives the SYN request. It responds with a SYN-ACK packet: Acknowledges the client's SYN (ACK = client's ISN + 1) Sends its own SYN with its own ISN. 📩 Example: Server sends: SYN, SEQ=2000, ACK=10013. ACK (Acknowledge) — Client → ServerThe client receives the server’s SYN/ACK. It sends a final ACK to: Acknowledge the server's SYN (ACK = server’s ISN + 1). Now the connection is established. 📩 Example: Client sends: CopyEditACK, SEQ=1001, ACK=2001✅ After the HandshakeAt this point, both the client and the server: Know that the other party is responsive. Have agreed on initial sequence numbers. Are ready to begin data transmission securely and reliably. 📊 VisualizationClient Server | -------- SYN --------> | | <----- SYN/ACK ------- | | -------- ACK --------> | | CONNECTION ESTABLISHED |🛡️ Related to CybersecurityUnderstanding the TCP handshake is critical for: Detecting SYN scans (common in port scanning). Analyzing traffic in tools like Wireshark. Detecting SYN Flood attacks, a type of Denial-of-Service (DoS) where the attacker floods the server with SYN packets without completing the handshake.
-
Understanding Port Scanning Techniques
🔍 Understanding Port Scanning TechniquesPort scanning is one of the most widely used reconnaissance techniques in ethical hacking and cybersecurity. It is used to identify open ports and services on a target system, giving attackers or security professionals insights into potential vulnerabilities. When a computer or server is connected to the internet or a local network, it runs various services (like web servers, email servers, or file transfer tools). Each service typically listens for requests on a specific port—for example, HTTP on port 80, HTTPS on port 443, FTP on port 21, and so on. 🧠 Why Port Scanning MattersAttackers use port scanning to find weak points in a system that may be exploitable. Security professionals use it to audit their networks and close unnecessary or dangerous ports. A port scan gives visibility into what’s exposed and potentially vulnerable on a system. 🧪 Types of Port Scanning TechniquesDifferent scanning methods reveal different levels of information and vary in how stealthy or aggressive they are: 1. Vanilla Scan (Full Connect Scan)This is the most basic scan, where the scanner attempts to establish a full TCP connection (3-way handshake) with every open port. It is easy to detect because it completes the handshake, thus showing up in logs. Tools: Nmap -sT Use case: Beginners, simple scans, or when stealth is not a concern. 2. Strobe ScanA strobe scan is a targeted scan, checking only a specific set of ports rather than scanning all 65,535. This makes it faster and slightly less noisy. Use case: Quick checks on known vulnerable services (e.g., SSH, RDP, HTTP). 3. Stealth Scan (Half-Open Scan / SYN Scan)This method sends a SYN packet to initiate a connection but does not complete the handshake. If the port is open, the system responds with a SYN-ACK, and the scanner sends a RST to tear down the connection before it's fully established. Harder to detect in logs compared to full connect. Use case: Penetration tests where stealth is important. Tools: Nmap -sS 4. FTP Bounce ScanUses a vulnerable FTP server to bounce scans to another system. The attacker can hide their real IP address by using the FTP server as a middleman. Rare today due to modern FTP servers closing this loophole. Use case: Bypassing firewalls or IDS that block direct scanning. 5. Fragmented Packets ScanBreaks the TCP header into smaller packet fragments, making it harder for firewalls or intrusion detection systems to inspect. Obfuscates scan traffic, useful for bypassing basic packet filters. Use case: Advanced stealth scanning or evading firewalls. 6. Sweep Scan (ICMP or TCP Sweep)Scans the same port across multiple IP addresses in a network to identify active hosts running a particular service. Helps attackers map a network. Use case: Scanning large subnets to find specific services (e.g., who runs port 3306 for MySQL?). 7. UDP ScanTargets UDP-based services like DNS (53), SNMP (161), or NTP (123). Since UDP is connectionless, it’s harder to detect whether the port is open. Often sends a UDP packet and waits for an ICMP “port unreachable” response. Use case: Finding services that don’t use TCP. Tools: Nmap -sU ⚠️ Ethical Consideration 🔧 Popular Tools for Port ScanningNmap (most widely used) Masscan (ultra-fast) Zenmap (GUI for Nmap) Unicornscan Netcat (nc) Port scanning is a critical step in both offensive and defensive security. By understanding different scanning methods, cybersecurity professionals can better detect, prevent, and respond to network threats. Whether you're a penetration tester or a network defender, mastering these techniques is essential for identifying and securing system vulnerabilities.
-
Best WordPress Security Plugins in 2025 to Protect Your Website from Hackers
🔐 Best WordPress Security Plugins in 2025 to Protect Your Website from HackersIf you're running a WordPress website in 2025, website security should be a top priority. With increasing cyber threats like brute force attacks, malware, and spam, it's essential to protect your site using reliable security plugins. Luckily, WordPress offers several plugins to help you detect, block, and prevent threats—even if you're not a cybersecurity expert. Here are the top WordPress security plugins for 2025 you can trust to keep your website safe and secure. 1. Wordfence SecurityWhy it's trusted: One of the most popular and comprehensive security plugins available. 🛡️ Firewall protection (WAF) 🔍 Malware scanner 🚨 Real-time threat defense feed 🔐 Two-factor authentication (2FA) 📬 Email alerts for suspicious activity Price: Free version available, Premium starts at $119/year Best for: Bloggers, small businesses, and e-commerce sites 2. iThemes Security (formerly Better WP Security)Why it's powerful: Offers over 30 security measures in one plugin. 🧠 Brute force protection 🚫 Bans known bad IPs 🔄 File change detection 🧪 Security logging and monitoring 🔒 Password policy enforcement Price: Free version available, Pro starts at $99/year Best for: Intermediate users and developers 3. Sucuri SecurityWhy it's trusted by pros: Developed by security experts. Focuses on post-hack security and prevention. 🔍 File integrity monitoring 📜 Security activity auditing 🔥 Web Application Firewall (WAF) available (paid) 📢 Alerts for security issues 🛠 Malware removal (Premium) Price: Free core plugin, full firewall starts at $199/year Best for: High-risk or high-traffic websites 4. All In One WP Security & FirewallWhy it’s great: User-friendly with visual indicators of security strength. 🧱 Basic firewall protection 🚫 Login lockdown & brute force protection 📊 Security strength meter 📁 File permissions & backup features Price: 100% Free Best for: Beginners and budget-conscious users 5. MalCare SecurityWhy it's efficient: Focuses on one-click malware removal with zero false positives. 🚀 Cloud-based malware scanning (no site slowdowns) 🔧 Auto-clean malware with one click 🛡️ Login protection and firewall 📅 Daily backups (with premium) Price: Free version available, Premium starts at $99/year Best for: Busy users who want hands-free security 6. Jetpack ProtectWhy it’s convenient: Comes bundled with other Jetpack features from WordPress.com. 🦠 Malware scanning and brute force protection 🔐 Secure login with two-factor authentication 📊 Simple dashboard integration with WordPress Price: Free for basic protection, Premium starts at $24/year Best for: WordPress.com users and casual bloggers ⚙️ Quick Comparison TablePlugin Firewall Malware Scanner 2FA Free Version Ease of Use Wordfence ✅ ✅ ✅ ✅ ⭐⭐⭐⭐ iThemes ✅ ✅ ✅ ✅ ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Sucuri ✅ (Pro) ✅ ❌ ✅ ⭐⭐⭐ All In One ✅ ✅ ✅ ✅ ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ MalCare ✅ ✅ ✅ ✅ ⭐⭐⭐⭐ Jetpack ✅ ✅ ✅ ✅ ⭐⭐⭐ 🛠️ Final Tips to Keep Your WordPress Site Secure✅ Use strong admin passwords 🔄 Update plugins and themes regularly 🔐 Enable 2FA for admin logins 🧱 Use a WAF (web application firewall) 🕵️♂️ Scan your site weekly 📦 Keep daily backups Conclusion Choosing the right security plugin is the first step toward protecting your WordPress site from cyber threats. Whether you're a blogger, an online store owner, or a developer, there's a plugin on this list that suits your needs. Have questions about setting one up? Drop a comment or message me for step-by-step help!
-
Best WordPress News Themes for 2025: Top Picks for Speed, SEO & Design
📰 Best WordPress News Themes for 2025: Top Picks for Speed, SEO & DesignIf you're planning to launch a news, magazine, or blog website in 2025, choosing the right WordPress theme is one of the most important steps. A great news theme should be fast, SEO-friendly, responsive, and easy to customize—and luckily, the WordPress ecosystem keeps evolving with some powerful options. Here’s a list of the best WordPress news themes in 2025 to help you build a professional news site with style and performance. 1. Newspaper X by tagDivWhy it's great: It’s the most popular news theme in the market—perfect for blogs, news, or magazine-style sites. 🔧 Built-in drag-and-drop page builder (tagDiv Composer) ⚡ Very fast loading & mobile-friendly 📌 Multiple pre-built demos (tech, politics, lifestyle, etc.) 💰 Price: Premium (around $59) Best for: News agencies, magazines, and high-traffic blogs 2. Astra + Elementor (Free + Pro)Why it's great: Astra is a lightweight multipurpose theme that works amazingly for news sites when combined with Elementor. 🚀 Super lightweight (loads in under 1 second) 🎨 Deep customization using Elementor or Gutenberg 🧠 SEO-optimized & schema-ready 💰 Free version available, Pro starts at $47/year Best for: Bloggers, tech news, small publishers 3. JNews by JegthemeWhy it's great: One of the most versatile themes for any type of content-based site. 🔄 AMP support for fast mobile experience 🔥 Built-in Google Ads & AdSense support 🎯 SEO and speed optimized 🎥 Supports video content well 💰 Premium (around $59) Best for: News websites with monetization and multimedia content 4. Zox NewsWhy it's great: Clean and bold design built for news and online magazines. 📰 Designed specifically for news readability 📲 Fully responsive and mobile-first design 💵 Monetization options built-in 💰 Premium (around $49) Best for: Independent news blogs, journalists, and content creators 5. Newsblock by CodesupplyWhy it's great: Modern theme with excellent typography and a clean interface. 🧩 Supports dark mode and multiple layout styles 📚 Gutenberg-ready 🚀 Optimized for Core Web Vitals (important for SEO) 💰 Premium (around $69) Best for: Tech news, crypto, finance, or niche blogs 6. GeneratePress (with GP Premium)Why it's great: Ultra-lightweight, flexible, and developer-friendly. 🔍 Focused on speed and SEO 🛠 Compatible with major page builders 🎨 Clean, minimalistic design 💰 Free version available, Premium is $59/year Best for: Publishers who want full control with minimal bloat 7. PenNews by PenciDesignWhy it's great: An all-in-one WordPress news theme with over 150 demos. 📺 Built-in video & audio playlist support 🧠 SEO schema, speed optimized, and mobile friendly 🎨 Comes with multiple ready-made templates 💰 Premium (around $59) Best for: Multi-category news websites ⚖️ Final Tips: How to Choose the Right ThemeWhen picking your news theme in 2025, consider: ✅ Speed & Performance – Choose lightweight themes for faster loading. ✅Customization – Look for themes with drag-and-drop support or full Gutenberg compatibility. ✅ Mobile Responsiveness – Most users will visit from phones. ✅SEO Features – Built-in schema and clean code improve ranking. ✅ Monetization Support – Ad spaces and compatibility with AdSense or affiliate tools. 📌 Pro Tip: Always test the theme’s demo on your mobile device and run it through tools like Google PageSpeed Insights before buying. Need help picking the perfect theme for your blog or news site? Drop a comment or message, and I’ll help you pick one based on your niche and goals.
-
How to Install Drupal by Yourself (Very Simple Step-by-Step Guide)
Hi everyone, In this post, I will show you how to install Drupal manually. If your hosting does not have an auto installer (like Softaculous), or you want to learn how to do it by yourself, this guide is for you. I will keep it very easy and step-by-step, using simple words so anyone can follow. ✅ Things You Need Before You StartBefore you can install Drupal, make sure you have these: A domain name (example: yourwebsite.com) A web hosting account (with cPanel or similar) File Manager or FTP access A MySQL database The Drupal zip file from the official website 📥 Step 1: Download DrupalGo to the official website: https://www.drupal.org/download Download the latest stable version of Drupal (choose the .zip file). Save the file on your computer. 📁 Step 2: Upload Drupal to Your HostingNow you need to upload Drupal to your website. 📌 Option 1: Use File Manager (Easy way)Login to your hosting control panel (like cPanel). Open File Manager. Go to the public_html folder (or the folder for your domain). Click Upload, and choose the Drupal zip file. After upload, right-click the file and choose Extract. You will get a folder named something like drupal-10.x. Open that folder, select all files, and move them to public_html. Delete the original Drupal folder and zip file to keep your files clean. 📌 Option 2: Use FTPYou can also use FTP software like FileZilla to upload the extracted files to public_html. 🛢️ Step 3: Create a MySQL DatabaseNow let’s create the database for Drupal. Login to your hosting control panel. Go to MySQL® Databases. Create a new database (e.g. drupaldb). Create a new database user and password. Add the user to the database and give All Privileges. 💡 Write down these details: Database name Database username Database password Database host (usually localhost) 🌍 Step 4: Start Drupal InstallationNow visit your website in your browser: https://yourdomain.com You will see the Drupal installation page. 🧾 Step 5: Choose LanguageSelect your preferred language (like English). Click Save and continue. ⚙️ Step 6: Choose Installation ProfileChoose Standard installation (good for beginners). Click Save and continue. 🗃️ Step 7: Set Up the DatabaseOn this page: Database Type → MySQL, MariaDB, or equivalent Database Name → Enter the name you created earlier Database Username → The user you created Database Password → The password you created Advanced Options → You can leave this part unless your host uses a different database host (use localhost usually) Click Save and continue. Drupal will now install. This may take a few minutes. 📝 Step 8: Site ConfigurationNow enter your website info: Site Name → Example: My Drupal Site Site Email Address → For alerts and password resets Admin Username → For logging in (e.g. admin) Admin Password → A strong password Confirm Password Default Country Time Zone Click Save and continue. 🎉 Step 9: You're Done!You should now see a page that says: You can now: Visit your site front page Go to the admin dashboard Admin dashboard URL is usually: https://yourdomain.com/user/login Login using the username and password you created. 🔧 What You Can Do NextAdd a theme (design) to change how your site looks Install modules to add features (like contact form, SEO, etc.) Create pages, blogs, and menus Set user roles and permissions 💡 TipsAlways update your Drupal when new versions come out Use strong passwords Don’t forget to make backups of your website often Drupal is a very powerful tool to build websites. Even though installing it manually looks hard, it becomes easy when you follow the steps slowly. If you need help or get stuck, feel free to reply below. I will do my best to help you out. Thank you for reading! 😊
-
How to Install Joomla Manually (Easy Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners)
Hello friends, In this post, I will teach you how to install Joomla manually. This means we will do everything by ourselves without using any auto installer like Softaculous. If you are a beginner, don’t worry. I will explain everything in a way that is very easy to understand. ✅ What You Need Before StartingBefore we begin, you need to have some things ready: A domain name (like yourwebsite.com) A web hosting account (where your site will live) Access to cPanel or hosting control panel Access to File Manager or FTP A MySQL database The Joomla installation zip file 📥 Step 1: Download JoomlaVisit the official Joomla website: https://downloads.joomla.org Download the latest Full Package (.zip) file. Save the zip file to your computer. 📁 Step 2: Upload Joomla FilesYou will now upload Joomla to your web hosting. 📌 Option 1: Using File ManagerLogin to your hosting control panel (like cPanel). Go to File Manager. Open the folder called public_html (this is your main website folder). Click Upload, and select the Joomla .zip file you downloaded. After uploading, extract (unzip) the file. The Joomla files will now appear in public_html. 📌 Option 2: Using FTP (like FileZilla)Connect using your FTP software. Go to the public_html directory. Upload and extract the Joomla files there. 🛢️ Step 3: Create a MySQL DatabaseNow we need to create a database that Joomla will use. In cPanel, find MySQL® Databases. Create a new database (example: joomdb). Create a new database user and password. Add the user to the database and give it all privileges. Write down this info: Database Name Database Username Database Password Hostname (usually localhost) 🌐 Step 4: Start the Joomla InstallationNow open your browser and go to your website: https://yourdomain.com You will see the Joomla installation screen. 🧾 Step 5: Configuration PageOn the first page, fill in your website details: Site Name → Example: My Joomla Site Description → A short sentence about your site Admin Email → Use your email Admin Username → Your login name (e.g. admin) Admin Password → Create a strong password Confirm Password → Type it again Click Next to continue. ⚙️ Step 6: Database SettingsOn the next screen: Database Type → MySQLi Host Name → localhost Username → Your database username Password → Your database password Database Name → The database name you created Table Prefix → Random letters (or use the one provided) Old Database Process → Leave it as is Click Next. 📊 Step 7: Final ReviewYou will now see a page with all the info you added. Scroll down and click Install. Joomla will now set up everything. This may take a few seconds. ✅ Step 8: Success PageOnce done, you will see: Before you continue, click the button to remove the “Installation folder”. This is important for security. Now you can choose: Visit your site → To see your new Joomla site Administrator → To login and manage your website 🔐 Login to Joomla Admin PanelTo manage your site, go to: https://yourdomain.com/administrator Enter your admin username and password to log in. 🛠️ What You Can Do NextChange the template (your website design) Add new articles (like blog posts or pages) Install plugins (to add features) Create menus and links Set up users and permissions Joomla is a powerful CMS, and installing it manually helps you understand how it works. If you follow this guide step by step, you will have Joomla working in no time. If you have any problem or question, feel free to ask below. I will try to help. Thanks for reading and good luck with your new website! 😊
-
How to Set Up WordPress Manually (Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners)
Hello everyone, Today I will show you how to install WordPress manually (by yourself). This is good if your hosting company does not have auto installer, or if you just want to learn how to do it by hand. Don't worry — I will make this post very simple and easy to follow. 🌐 What You Need Before You StartBefore you install WordPress, make sure you have these: A domain name (like mywebsite.com) A hosting account (where your website will live) A file manager or FTP access (to upload files) A MySQL database (for WordPress to save data) WordPress zip file (you can get this from wordpress.org) 🧱 Step 1: Download WordPressGo to this website: https://wordpress.org/download/ Click the button that says Download WordPress. It will download a zip file to your computer. 📁 Step 2: Upload WordPress to Your HostingYou can use: File Manager (in cPanel or your hosting dashboard), OR FTP software like FileZilla. 📌 Using File Manager:Login to your hosting control panel (like cPanel). Go to File Manager. Open the folder called public_html (this is your main website folder). Click Upload, and upload the WordPress zip file you downloaded. After upload, extract (unzip) the file. Now you will see a folder named wordpress. Open it, select all files, and move them to public_html. After moving, you can delete the wordpress folder and the zip file to keep things clean. 🛢️ Step 3: Create a MySQL DatabaseIn your hosting panel (like cPanel), look for MySQL® Databases. Create a new database. Give it a name (example: mydb). Create a new database user and a strong password. Add the user to the database and give it All Privileges. Please write down these: Database Name Database User Password Database Host (usually it is localhost) You will need them soon. 🧠 Step 4: Set Up WordPressNow go to your website URL. Example: https://yourdomain.comYou will see the WordPress installation page. Select Your LanguageChoose your language (like English) and click Continue. Database Setup PageYou will see a page asking for: Database Name → (use the one you created) Database Username → (use the one you created) Database Password → (use the one you created) Database Host → usually localhost Table Prefix → just leave it as wp_ Click Submit. If everything is correct, you will see a message: "All right, sparky!" Click Run the installation. 📝 Step 5: Fill in Website DetailsNow you need to set your website info: Site Title → (example: My First Blog) Username → (you will use this to login) Password → (create a strong one) Email → (for recovery and alerts) Leave the checkbox for Search Engine Visibility if you don’t want Google to find your site yet. Click Install WordPress. ✅ Step 6: You're Done!You will now see: Click the Log In button and use the username and password you just created. 🛠️ Some Extra TipsTo go to your website, visit: https://yourdomain.com To log in to admin panel, go to: https://yourdomain.com/wp-admin From your dashboard, you can change themes, install plugins, write blog posts, and more! Installing WordPress manually may look hard at first, but if you follow the steps one by one, it's not too difficult. Now you can build your blog, business website, or any type of site you want! If you have any questions, reply below and I will try to help. Thanks for reading!